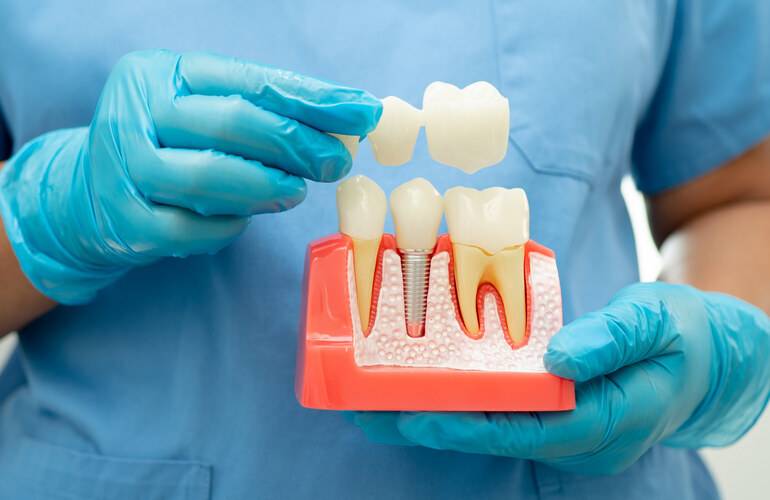
Explanation of what a dental crown is
A dental crown is a custom-made cap placed over a tooth to restore its shape, size, strength, and function. Crowns are commonly used to protect weak teeth, restore broken or worn-down teeth, or improve aesthetics. They play a crucial role in modern dentistry, offering both restorative and cosmetic benefits.Crowns can be necessary after a root canal treatment, when a tooth has been severely damaged by decay or injury, or when a large filling has compromised the tooth’s structure. They help restore the ability to chew and speak properly while also preventing further damage.
Materials used for dental crowns
Dental crowns can be made from a variety of materials, each offering unique advantages. The most common materials include:
- Porcelain or Ceramic: These crowns provide a natural look and are ideal for front teeth. They mimic the translucency of real teeth and are highly aesthetic.
- Metal (Gold or Silver): Metal crowns are extremely durable and resistant to wear. They are often used for molars, where strength is a priority over appearance.
- Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM): This type combines strength with aesthetics. However, over time, the metal beneath the porcelain may become visible as a dark line at the gumline.
- Zirconia: A relatively new material, zirconia is both strong and aesthetically pleasing. It is often used for both front and back teeth and is highly resistant to fractures.
- Resin: A more affordable option, resin crowns are less durable than other materials but can be a cost-effective solution for those on a budget.
Purpose and function of dental crowns
Dental crowns serve several important functions, including:
- Strengthening weak or fractured teeth.
- Protecting a tooth after a root canal.
- Restoring broken or severely decayed teeth.
- Covering dental implants.
- Enhancing the appearance of discolored or misshapen teeth.
- Supporting dental bridges to replace missing teeth.
Types of dental crowns
Permanent vs. temporary crowns
- Temporary Crowns: Made of acrylic or stainless steel, these are used as a short-term solution while waiting for the permanent crown.
- Permanent Crowns: Custom-made from durable materials and designed to last for several years with proper care.
Different materials and their benefits
Each material has its own advantages:
- Porcelain: Best for aesthetics, blending with natural teeth.
- Gold or Silver: Extremely durable, suitable for high-bite pressure areas.
- Zirconia: A balance between durability and aesthetics, resistant to wear.
- Resin: Affordable but less long-lasting than other options.
Customization options for crowns
Crowns can be customized based on:
- Color: Matching the shade of adjacent teeth.
- Shape and Size: Designed to fit perfectly in the mouth.
- Material Preference: Based on durability and aesthetic needs.
Reasons for getting a dental crown
Restoration of damaged or decayed teeth
Teeth that have suffered from extensive decay or fractures may need crowns to restore their function and structure. Crowns help prevent further damage and can extend the lifespan of the natural tooth.
Protection after root canal treatment
A root canal-treated tooth is more fragile and requires a crown to prevent breakage and ensure longevity. Without a crown, the tooth may weaken and eventually need extraction.
Cosmetic improvements and aesthetic reasons
Crowns are used to cover discolored, misshapen, or uneven teeth, enhancing the overall smile. Many patients opt for crowns as part of a smile makeover to improve their confidence.
The dental crown procedure
Initial consultation and assessment
During the first appointment, the dentist will examine the tooth, discuss material options, and take X-rays to assess the underlying structure. This step helps determine whether a crown is the best option or if additional treatments are needed.
Tooth preparation and impression taking
- A portion of the tooth is trimmed to make space for the crown.
- Impressions are taken to create a custom-fit crown, which is then sent to a dental lab.
Temporary crown placement and final fitting
- A temporary crown is placed to protect the tooth while the permanent one is fabricated.
- Once ready, the permanent crown is bonded, adjusted, and polished for a natural fit.
Benefits of dental crowns
- Restores functionality, allowing normal chewing and speaking.
- Enhances the appearance of the smile.
- Provides long-term durability with proper care.
- Prevents further tooth damage or decay.
- Covers and strengthens weak or damaged teeth.
- Can be customized for a natural and comfortable fit.
How to take care of your dental crowns?
Maintenance tips for longevity of the crown
- Avoid chewing hard foods like ice and nuts to prevent chipping.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups to ensure the crown remains intact.
- Wear a night guard if you grind your teeth.
Recommended oral hygiene practices
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss regularly to prevent plaque buildup around the crown.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce the risk of infections.
Cost considerations for dental crowns
Factors affecting the cost of dental crowns
The cost of a dental crown varies based on several factors:
- Material Used: Porcelain and zirconia crowns are more expensive than resin.
- Complexity of the Procedure: Additional treatments like root canals can increase costs.
- Geographic Location: Prices vary based on the region and the dentist’s expertise.
Insurance coverage and financing options
- Many dental insurance plans cover a portion of the cost of crowns if they are medically necessary.
- Payment plans and financing options may be available through dental offices to make the procedure more affordable.
A dental crown is a reliable and long-lasting solution for protecting and restoring damaged teeth.

Josaida Contreras is a Doctor of Dental Surgery and Endodontics specialist with nearly 20 years of experience. Educated in both Latin America and the U.S., she continues to expand her expertise through advanced training in implant dentistry.